-
The Rendering Pipeline - Tessellation카테고리 없음 2024. 2. 4. 22:27
Hull Shader
Hull Shader
- Provide the tessellator with how small the input geometry will be split.
- Provide the domain shader with processed control patch primitives.
- Two HLSL functions of hull shader
- Main function
- Executed by the number of control points required to generate one output control patch.
- Output one control patch per execution.
- Patch constant function
- Executed once for each complete control patch.
- Define tessellation coefficients, which used to subdivide patches.
- Main function
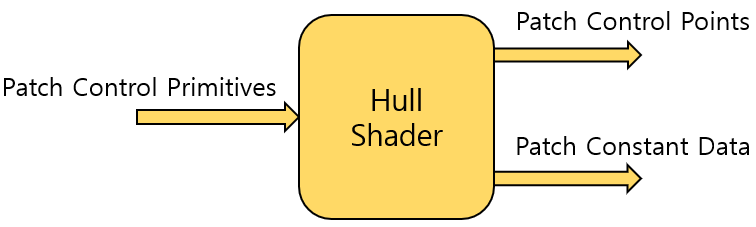
The structure of hull shader Input of Hull Shader
- Control patch primitives
- The vertex set as a result of the vertex shader + the primitive stream of input assembler
- Two parameters of input control patch
- Format of data calculated by vertex shader
- The number of control points in the input control patch
- SV_OutputControlPointID
- Index of the control point that caused the current hull shader program to be executed.
- Unsigned integer, $\le$ the size of the output control patch.
- SV_PrimitiveID
- Identify the current primitive. (more specifically, the control patch)
- Unsigned integer
Status Description of Hull Shader
- Shader program
- ID3D11DeviceContext::HSSetShader()
- The definition of the patch constant function and the list of function level attributes must come before
- Constant buffer
- ID3D11DeviceContext::HSSetConstantBuffers()
- The main means of providing data to the hull shader program.
- Shader resource view
- ID3D11DeviceContext::HSSetShaderResources()
- A means of providing read-only data to the hull shader program.
- Sampler status object
- ID3D11DeviceContext::HSSetSamplers()
- Provide the ability to perform various filitering operation when reading texels from a texture resource.
- Function attribute : individual sentences that change specific settings of the tessellation system.
// Designate the domain of the primitive to be tessellated [domain("tri")] // Designate a tessellation method [partitioning("fractional_even")] // Designate the type of primitive to be generated through tessellation [outputtopology("triangle_cw")] // Designate the number of control points that the hull shader wants to create [outputcontrolpoints(3)] // Designate the patch constant function by the name of function [patchconstantfunc("PassThroughConstantHS")] // Designate the maximum value of the tessellation coefficient [maxtessfactor(5)]Process of Hull Shader
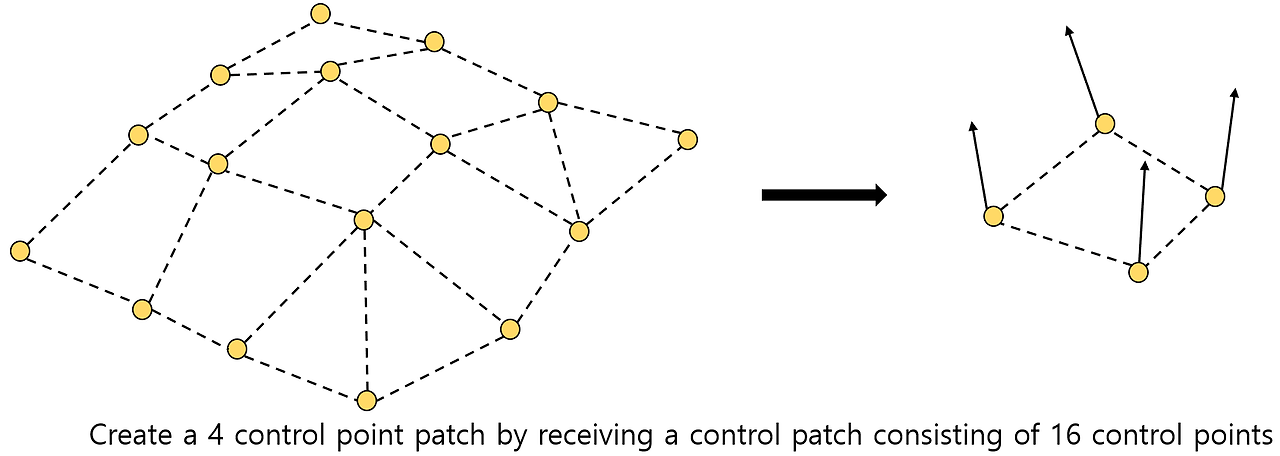
- Hull shader program (main function)
- Receive all control points in the input control patch primitives as one input attribute.
- Calculate an appropriate number of output control points.
- Setting up a tesslation algorithm
- Possible to change, expand, and reduce the shape of the input control patch.
- Replace the tessllation algorithm without affecting the rest of the pipeline.
- Detailed level of the tessellation algorithm
- Objects close to the camera : more sophisticated tessellation algorithm
- Objects far away from the camera : less complex tessellation algrorithm
- General control point calculation : suitable place to calculate values that will be commonly applied to several tessellated points
- Calculate the coefficient of tessellation. (patch constant function)
Output of Hull Shader
- Hull shader program
- Output control points constituting the control patch to be used for tessellation.
- No system value that must be printed out.
- Patch constant function
- Calculate the appropriate number of tessellation coefficients.
- Output tessellation coefficients through SV_TessFactor and SV_InsideTessFactor.
- Provide all patch constant information through the output attributes.
Tessellator
Tessellator
- The only fixed-function stage among pipeline stages that perform tessellation.
- Perform tessellation as much as tessellation coefficients that the patch constant function designate.
- Create a set of coordinates points within the current 'domain'
Input of Tessellator
- Input of tessellator : the coefficients of tessellation created by the patch constant fucntion of the hull shader stage through 'calculation'.
- The output is exactly the same if the inputs are the same, regardless of how the tessellation coefficients are calculated.
Status Description of Tessellator
- Designated through the function attributes of the hull shader program, not application program.
- [domain] attributes
- Determine the points in the domain corresponding to the [domain] attribute.
- Available value : isoline, tri, quad
- Must be specified because it is also used to check whether the number of tessellation coefficients is valid.
- [partitioning] attributes
- Specify a method of partitioning a designated domain.
- Available value : integer, fractional_even, fractional_odd, pow2
- Essential attributes that cannot be omitted.
- [outputtopology] attributes
- Designate the type of primitive to form.
- Available value : triangle_cw, triangle_ccw, line
- Essential attributes that cannot be omitted.
- [maxtessfactor] attributes
- Specify the maximum value of a tessellation coefficient.
- Used when the driver efficiently preallocates enough memory to contain the results of the tessellation operation.
Process of Tessellator
- Process of tessellator
- Select a series of points within a given domain.
- Use the points to create primitives.
- Provide the primitives to the next stages of the pipeline.
- Sample positions
- Select the tessellation points to create an appropriate number of triangles.
- More points are selected for the larger portion of the edge and the inner tessellation coefficient.
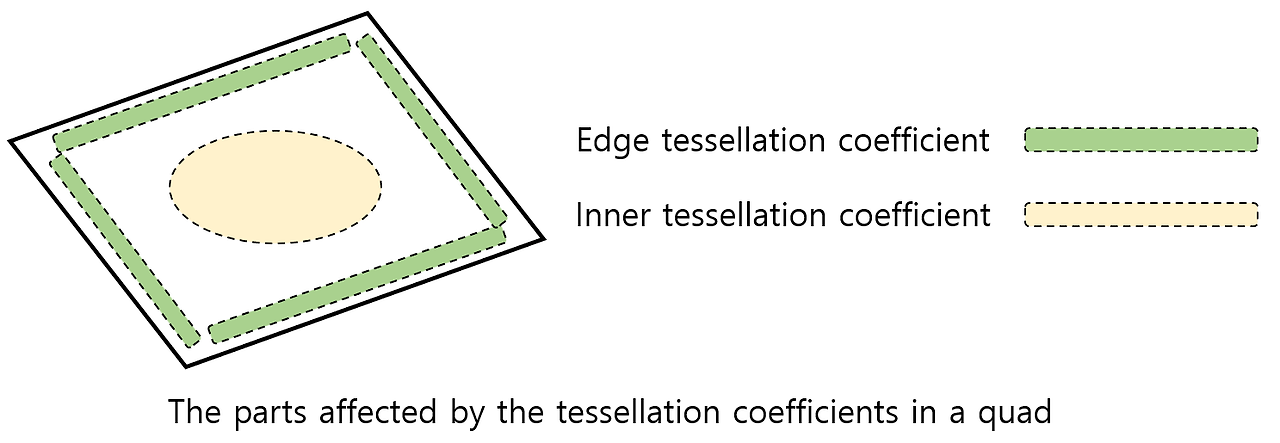
- Creation of primitives
- Create the selected sample positions as primitve information necessary for subsequent stages in the pipeline to use as a renderable geometry.
- The [outputtopology] attribute should not contradict the culling setting used in the rasterizer, in order to ensure that visibility determination occurs properly.
Output of Tessellator
- SV_DomainLocation : output texture coordinates
- For each domain coordinate point, one SV_DaminLocation is transferred to the domain shader stage.
- Primitive topology
- Delivered directly to the geometry shader without being used by the domain shader.
- The type of primitive containing adjacent information cannot be transferred to the geometry shader.
- Calculation requiring adjacent information may be performed by the hull shader or the domain shader.
Domain Shader
Domain Shader
- The last stage of the tessellation system.
- The stage of performing practical tessellation operations by applying tessellation algorithm set by hull shader to locations created by the tessellator.
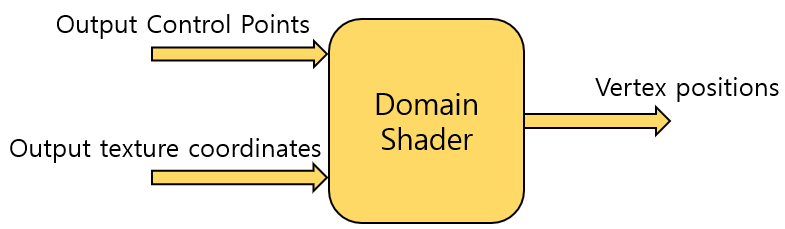
The structure of domain shader Input of Domain Shader
- SV_DomainLocation system value semantic
- The coordinate points created by the tessellator stage.
- The domain shader stage is executed once for each coordinate point.
- The completed control patch calculated by the hull shader stage
- The number of control points must match the number specified in the [outputcontrolpoints] function attribute of the hull shader program.
Status Description of Domain Shader
- Shader program : ID3D11DeviceContext::DSSetShader()
- Constant buffer : ID3D11DeviceContext::DSSetConstantBuffers()
- Shader resource view : ID3D11DeviceContext::DSSetShaderResources()
- Sampler status object : ID3D11DeviceContext::DSSetSamplers()
Process of Domain Shader
- Create vertices using a set of coordinate points, control patches and patch constants.
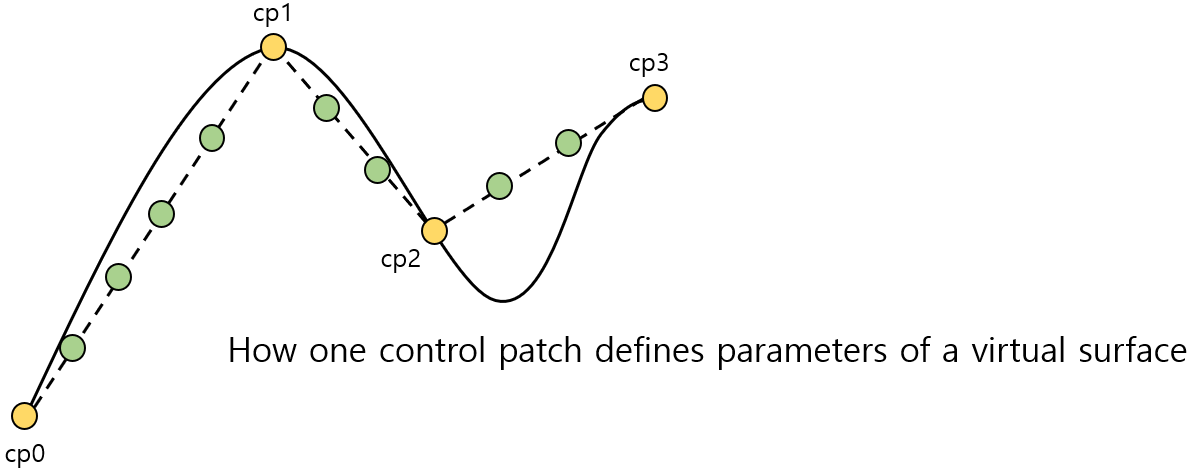
- The overall tessellation process is designed by dividing it into several components.
- Must create a control patch that defines the surface (curved) we actually want.
- Necessary to calculate the tessellation coefficients that minimize the number of required vertices while properly sampling the desired curved surface.
- Should implement algorithms to properly sample virtual surfaces from control patch data using a given set of coordinate points.
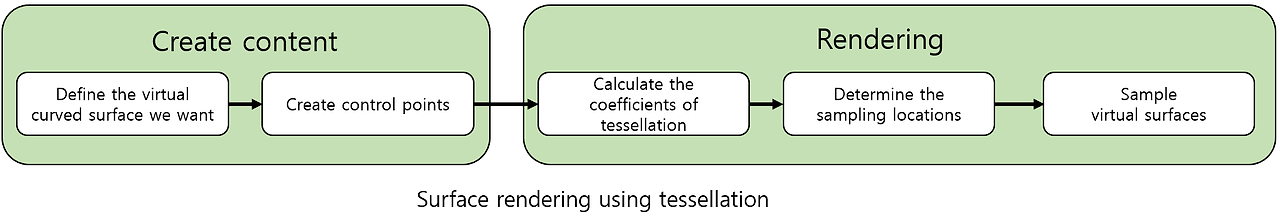
Output of Domain Shader
- The output vertex completed by calculating the required attribute data.
- SV_Position : include the position of the output vertex.
- Other vertex-specific attributes required to determine the final pixel color.