-
SynchronizationCS/OS 2024. 4. 21. 23:03
Race Condition
Synchronization
- Solve problem causing by accessing to shared resources.
- Without synchronization, it lead to incorrect results, called race condition.
- A way to coordinate threads (or processes) that use shared resources or their execution for correctness.
- Goal of synchronization is ensuring correct operation of cooperating threads.
Race Condition
- The result by threads accessing shared resources is non-deterministic. (Incorrect error)
- Depend on timing of execution. (multithreaded / multiprocessor system)
- Hard to access the shared resources in an atomic operation.
- Atomic operation : Non-interruptible operation
Critical Section
- A piece of code that accesses a shared resource.
- Entry section : permission to enter the section. (lock)
- Critical section (Atomic)
- Exit section : unlock
- Problem : to design a protocol that the processes can use to cooperate.
Critical Section Problem Solution
- Mutual Exclusion : critical section에 동시에 여러 개의 thread 혹은 process가 접근
- Progress : critical section이 empty and waiting인 경우
- Bounded waiting : 어떤 process 혹은 thread가 starvation 되는 경우
SW Approach
Naïve Approach

- Only implement a simple flag to keep track of possession of a lock.
SW Approach (1)

- Synchronization variable : global variable Turn
- int turn; Initially turn = 0;
SW Approach (2)

- Synchronization variable : Each flag
- Boolean flag[2] = { false, false };
Peterson's Algorithm

- Combined synchronization variables of algorithm (1), (2).
- Meets all three requirements.
- 그러나 $N \ge 3$일 경우, 만족 못 할 수도 있음.
- Shortcomings : busy waiting (spin lock), implementation difficulty, uniprocessors (could disable interrupts), disable preemption
HW Support
Disabling Interrupt

- Pros : simplicity
- Cons
- 인터럽트를 받을 수 없으므로, 시스템 자원을 효율적으로 사용할 수 없음.
- These privileged operations can be abused by some malicious programs (보안 문제)
- The approach does not work on multiprocessors.
TAS (Test-And-Set)

- Makes both test (load) and set (store) a single atomic operation.
- Test : checks the old lock value.
- Set : sets the lock to the new value.
CAS (Compare-And-Swap)

- Another HW primitive for locks.
- Similar lock implementation to that with test-and-set.
Spin Lock
- Only allows a single thread to enter the critical section at a time. (mutual exclusion)
- Don't provide any fairness guarantees and may lead to starvation.
- On single-processor : waste CPU cycles during spinning (busy-waiting)
- On multiprocessor
- Don't waste many CPU cycles.
- Spinning to wait for lock held to another processor.
Semaphore
- Critical section problem solution or condition variable.
- 구성
- Semaphore $S$
- init operation : Initialize a semaphore.
- semWait operation : decrements the value.
- semSignal operation : increments the value.

- Implementation with no busy waiting
- To avoid busy waiting, a semaphore may use an associated queue (blocked queue) of processes that are waiting on the semaphore.
- Sleep-and-Awake 기법 사용.
- Binary semaphore
- Integer value can range only between 0 and 1 to use as a lock.
- 0 / 1 or (lockded / unlockded, unavailable / available)
- Also known as mutex locks.

- Counting semaphore
- Integer value can range over an unrestricted domain.
- Also known as general semaphore.

- Implementations of semaphores (semaphore 변수 또한 shared data)

Locks in Linux

- Two-phase lock approach
- A hybrid approach to locks.
- First phase : spin lock
- Second phase : block the thread (sleep)
- Use futex support to sleep and wake processes in kernel space wait queue.
- futex_wait(address, expected)
- futex_awake(address)
Condition Variables

- Important synchronization primitive beyond locks.
- Basic requirements of using condition variables properly
- State variable
- Lock for the state variable
- Loop checking a condition using state variable
Producer and Consumer Problem
- It is also known as bounded buffer problem.
- Mutual exclusion by mutex.
- Mesa semantics : the woken thread should re-check the state variable after it wakes up.
- Using two condition variables : empty condition, fill condition.
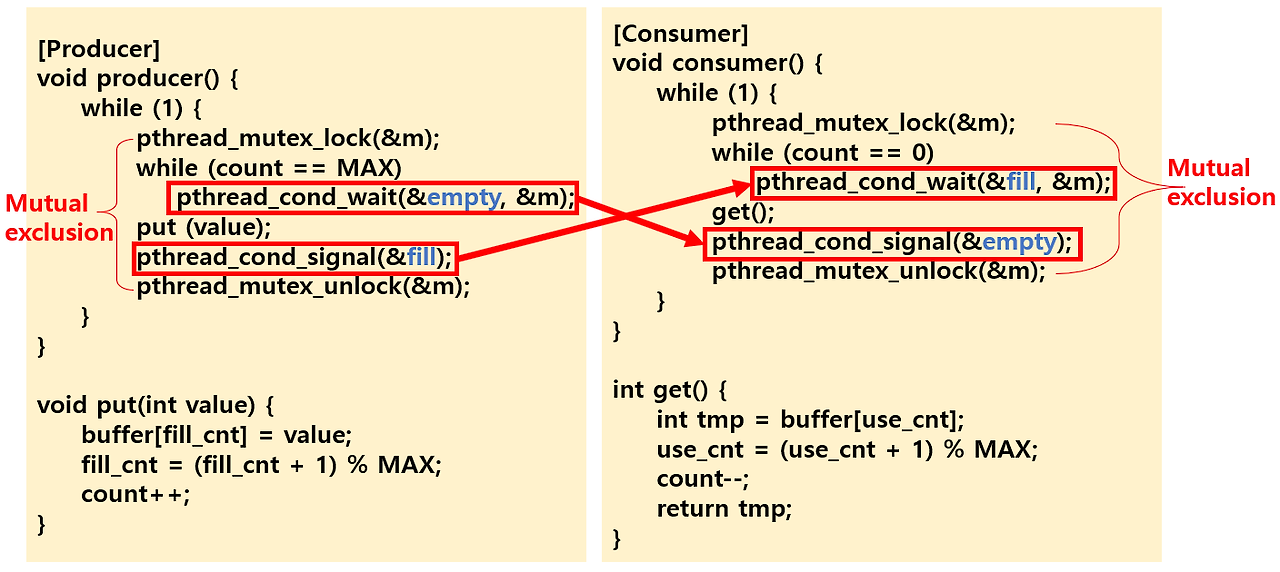
Solution with pthread 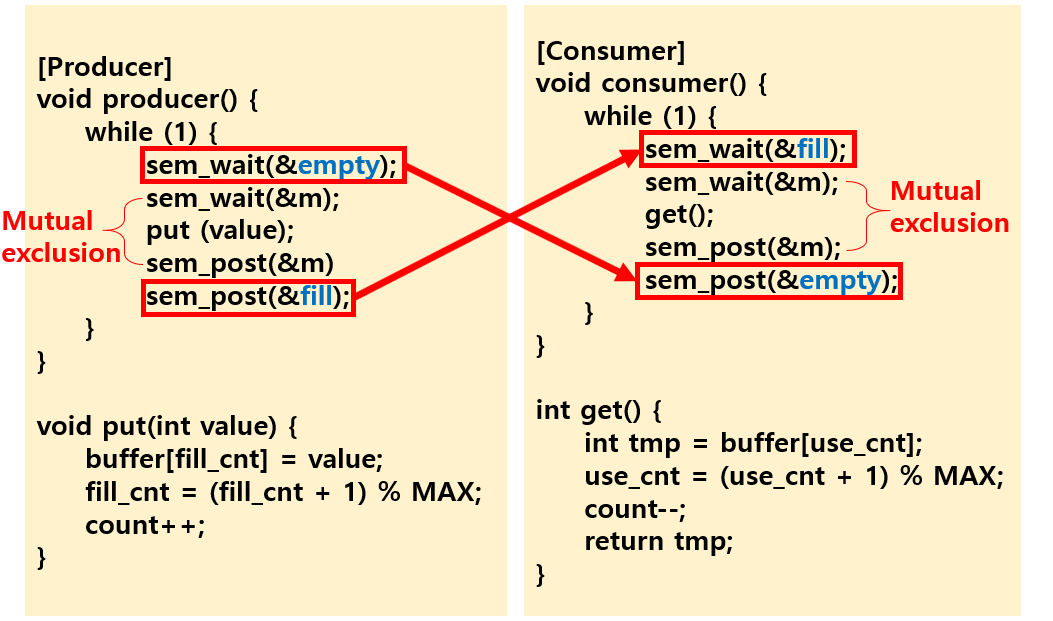
Solution with semaphore Monitor in Java
- Problem of semaphore
- Difficult to code.
- Difficult to prove correctness.
- Requires voluntary cooperation.
- Deadlock.
- A high-level abstraction that provides a convenient and effective mechanism for process synchronization.
- A thread-safe class, object, or module in order to safely allow access to a procedure or variable while retaining the advantage of a structured contruct.

Reads and Writers Problem
- A data set is shared among a number of concurrent processes.
- Readers : only read the data set; they do not perform any updates.
- Writers : can both read and write.
- Problem
- Only one single writer can access the shared data at the same time.
- Allow multiple readers to read at the same time.
- Shared data
- DB
- int readCount = 0; (number of readers)
- Synchronization variable
- Semaphore wsem initialized to 1 for DB
- Semaphore x initialized to 1 for readcount
- 효율성 제고
- Reader는 데이터를 수정하지 않음.
- 몇 개의 Reader가 critical section에 동시에 들어가도 데이터 일관성(data consistency)는 유지.
- Writer와 Reader끼리는 mutual exclusion 유지
- Reader끼리는 shared data에 동시 접근 허용
'CS > OS' 카테고리의 다른 글
Threads (0) 2024.04.17 Process Scheduling 2 (0) 2024.03.20 Process Scheduling 1 (0) 2024.03.13 Process Description and Control (0) 2024.03.06 User Program and System Call (0) 2024.03.06