-
Process Description and ControlCS/OS 2024. 3. 6. 19:54
Terminologies : Program and Process
Program vs Process
- Program : passive entity stored stored on disk (binary sequence)
- Process : active entity (execution sequence)
- Program becomes process when executable file loaded into memory
- Two essential elements of a process
- Program code
- A set of data associated with that code
Process
- A program in execution
- The entity that can be assigned to and executed on a processor
- A unit of activity characterized by the execution of
- a sequence of instructions
- a current state
- an associated set of system resources
Execution Sequence (Process) and Stack
- Common technique for controlling the execution sequence
- Stack : LIFO list (runtime context)
- Call stack : a stack data structure of a program, returning address on stack (set of stack frames)
- Implementation of stack
- Stack pointer : contains the address of the current top of the stack $$Stack \ Base \ (Higher \ Addr.) \ \le \ SP \ \le \ Stack \ Limit$$
- Stack frame
- Return address
- Parameters to be passed to the called procedure
- Return values
- Local variables
- Previous frame pointer
Process Description (Process Context)
- System-level context : Process Control Block (PCB)
- Process identification
- Processor state information
- Process control information
- User-level context (memory) : user text, user data, user stack (run-time context)
- Hardware context (register)
- Consists of the contents of registers
- Special-purpose registers (PC, SP, PSW...) + general-purpose registers
Process Image and Process Control Block
Process Image
- OS maintains a prcess image as a description of each process
- User data, user program, stack (user stack + kernel stack), process control block
Process Control Block
- Process identification : unique identifiers (pid, uid, ppid...)
- Processor state information : the contents of processor registers
- Process control information : needed by the OS to control the processes
- Process relation : 프로세스 관계에 대한 포인터 정보
- Process state : RUN, READY, BLOCK
- Scheduling information : policy, priority, need_resched
- Memory information : segment, page
- File information : file descriptor
- Role of the PCB
- The most important data structure in an OS
- Difficulty is not access, but protection
Process States
Two-State Process Model

Flow of two-state process model Five-State Process Model
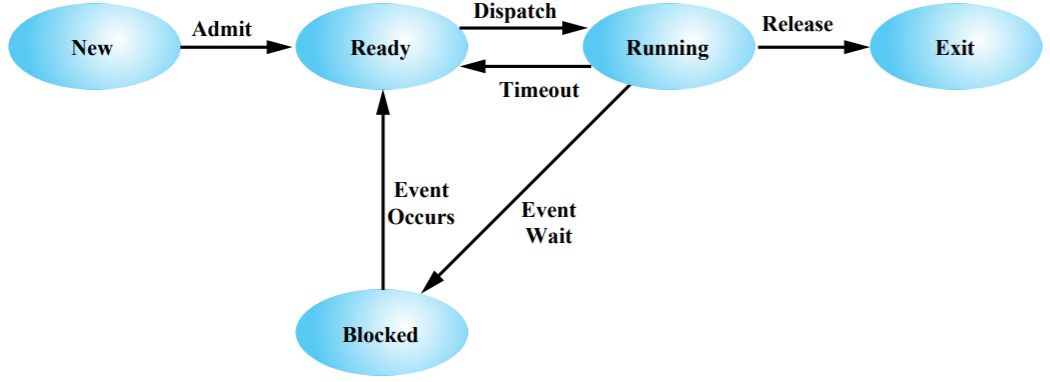
Flow of five-state process model - New : created
- Running : executed
- Blocked (Waiting) : waiting for some event to occur
- Ready : waiting to be assigned
- Exit (Terminated) : finish execution
Seven-State Process Model
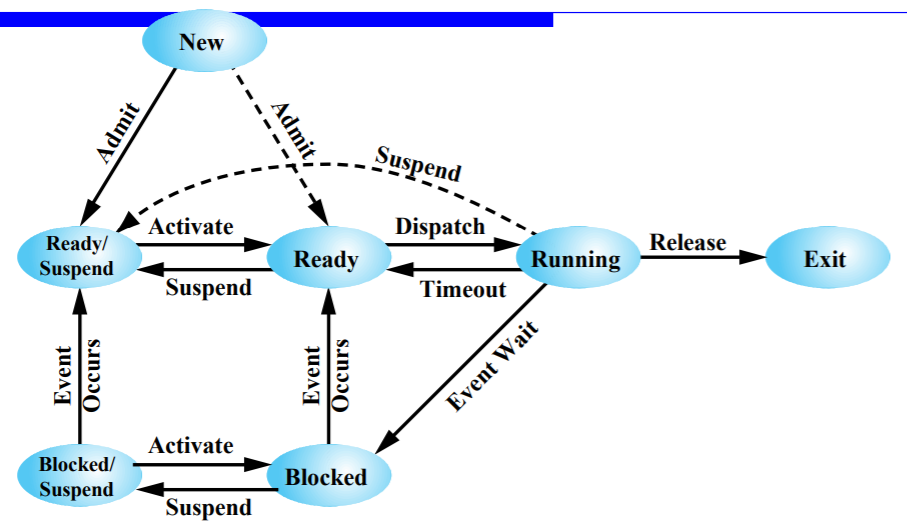
Flow of seven-state process model - Swapping : Blocked / Suspend, Read / Suspend -> secondary memory에 존재
Terminologies : mode switch and process switch
- Mode switch : switching the processor between user mode and kernel mode
- Process switch (context switch) : switching the processor from one process to another
- Process switch overhead
- PCB update
- Saving / Restoring contexts into / from PCB
- Update the process state
- Scheduling overhead : finding the next process to execute
- Memory
- TLB needs to be reloaded (MMU)
- Loss of cache locality : more cache misses
- PCB update
Execution Model of OS
Nonprocess Kernel
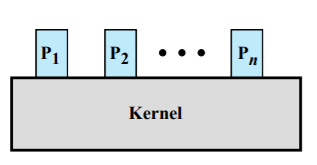
- Kernel is executed as a separate entity
Execution within User Processes (Common in OS)

- Execute all OS functions in the context of a user process
- Each process image includes program, data, and stack for kernel
- A separate kernel stack is used while the process is in kernel mode
Process-Based Operating System (Modular OS)

- Some noncritical OS functions are implemented as separate processes
Kernel Stack

- Each process has 2 stacks
- User space stack : used when executing user code
- Kernel space stack : used when kernel code in the context of a process
- Advantage : 시스템을 보호하기 위해, 즉 안정성을 높이기 위함 (Dual mode와 같은 취지)
Process Creation
Directed
- Init process 생성하기 위해 사용
- Allocate a new memory space
- Load code and data into the new memory space
- Create call stack
- Initialize PCB
- Start the new process, by putting process on ready-queue
Cloning
- 대부분 Process를 생성하기 위해 사용 (Parent Process를 copy)
- Use fork() system call (Called "Process Spawning")
- Make a copy of text, data, stack and PCB
- Modify the pid, relation...
- Add new PCB to ready-queue
Copy on Write (COW) Mechanism
- After fork : share the memory
- After write operations : copy the page when data is any of the shared page change
- 즉, 모든 부분을 Copy하기엔 Overhead가 크기 때문에 변경된 Data 발생 시에 부분적으로 Copy
Separate Processes (fork + exec)
- A way to create a typical process
- Two step : first fork() and exec()
- Child duplicate of parent : fork()
- Child has a program loaded into it : exec()
- Exec system call : replace the process's memory space with a new program

Execution options
- Parent and children execute concurrently (백그라운드 실행)
- Parent waits until children terminate : wait() system call
// status : process 종료 상태 pid = wait(&status);Process Switch

Flow of process switch - P executes the first instruction
- System call : software interrupt
- Jump to sys_yield in kernel
- PC : dedicated sys_xxx() kernel function in system call table
- SP : setup kernel stack and point top of kernel stack
- PSW : transition to kernel mode
- Save current process P's context to P's PCB
- Restore another process's context (Q)
- Q executes it's instruction
- Resume process P by loading context from PCB
- Recall : PC was pointing at return from save_context, so return back to process_switch()
- sys_yield returns back to process P
- Reset CPU to user mode
Process Termination
Voluntary Termination
- exit(status) : 정상 종료
- Result in the process termination
- exit() system call
- Output data from child to parent (via wait())
- Process's resources are deallocated by OS
Involuntary Termination
- kill(pid, signal) or abort() : 비정상 / 강제 종료
- Called by another process (parent) or by the OS
- A signal that the process needs to be killed
- Zombie process : PCB in OS still exists even though program is no longer execution
- Occur when a child process terminates before its parent
- Parent process can read the child's exit status via wait()
- After parent reads status, zombie entries are removed from OS
- If parent doesn't read status, it will continue to exist
- Reaper process : periodically runs and recovers
- Orphan Process
- Occur when a parent process terminates before its child
- Adopted by first process (init process)
'CS > OS' 카테고리의 다른 글
Threads (0) 2024.04.17 Process Scheduling 2 (0) 2024.03.20 Process Scheduling 1 (0) 2024.03.13 User Program and System Call (0) 2024.03.06 Computer System Overview (0) 2024.02.26